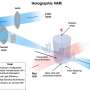
While traditional 3D printers work by depositing layers of material, tomographic volumetric additive manufacturing (TVAM) involves shining laser light at a rotating vial of resin until it hardens where accumulated energy exceeds a certain threshold. An advantage of TVAM is that it can produce objects in a matter of seconds, compared to around 10 minutes for layer-based 3D printing. But a disadvantage is that it is very inefficient, because only around 1% of the encoded light reaches the resin to produce the desired shape.
Author Details

Anna Riley
Members of Kanta Dab Dab, a band specialising in fusion of local Nepali and Western music elements, talk about their…
Follow Us
Popular Tags
Top Categories
- Uncategorized (6,413)

Leave a Reply